Combination Deep Diffractive Neural Networks
Deep Diffractive Neural Networks
Deep Learning as become a basic tool for image classification. Training and testing using Deep Neural Networks is an incredibly time-consuming and resource-heavy process, especially for large image datasets. Recent advances in Deep Learning Diffractive Optics have shown to potential to alleviate these problems by embedding software into hardware. Specifically, Trabelsi et al. demonstrated that a Neural Network can be trained using all complex values instead of all real values for audio applications by using basic convolutional neural network building blocks [1]. Using this result, Lin et al. successfully demonstrated image classification using a terahertz source and 3-D printed passive diffractive layers. To accomplish this, Lin et al. presented a theoretically linear network, called D2NN, by modulating complex electric fields by complex valued transmission and reflection coefficients. Thus, allowing the forward propagation step to be computed at the at light speed with great empirical accuracy, albeit linear, for the MNIST Handwritten Dataset and the MNIST Fashion Dataset [2].
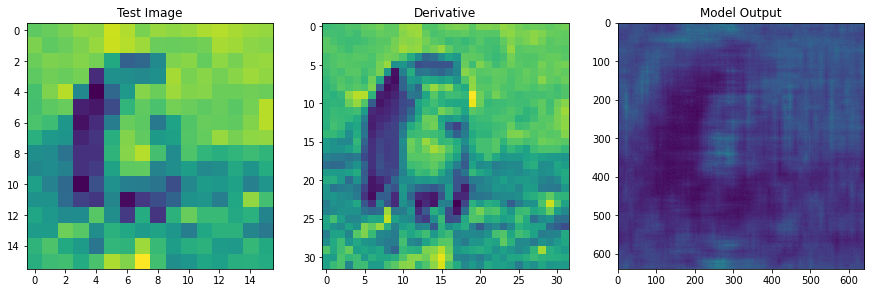
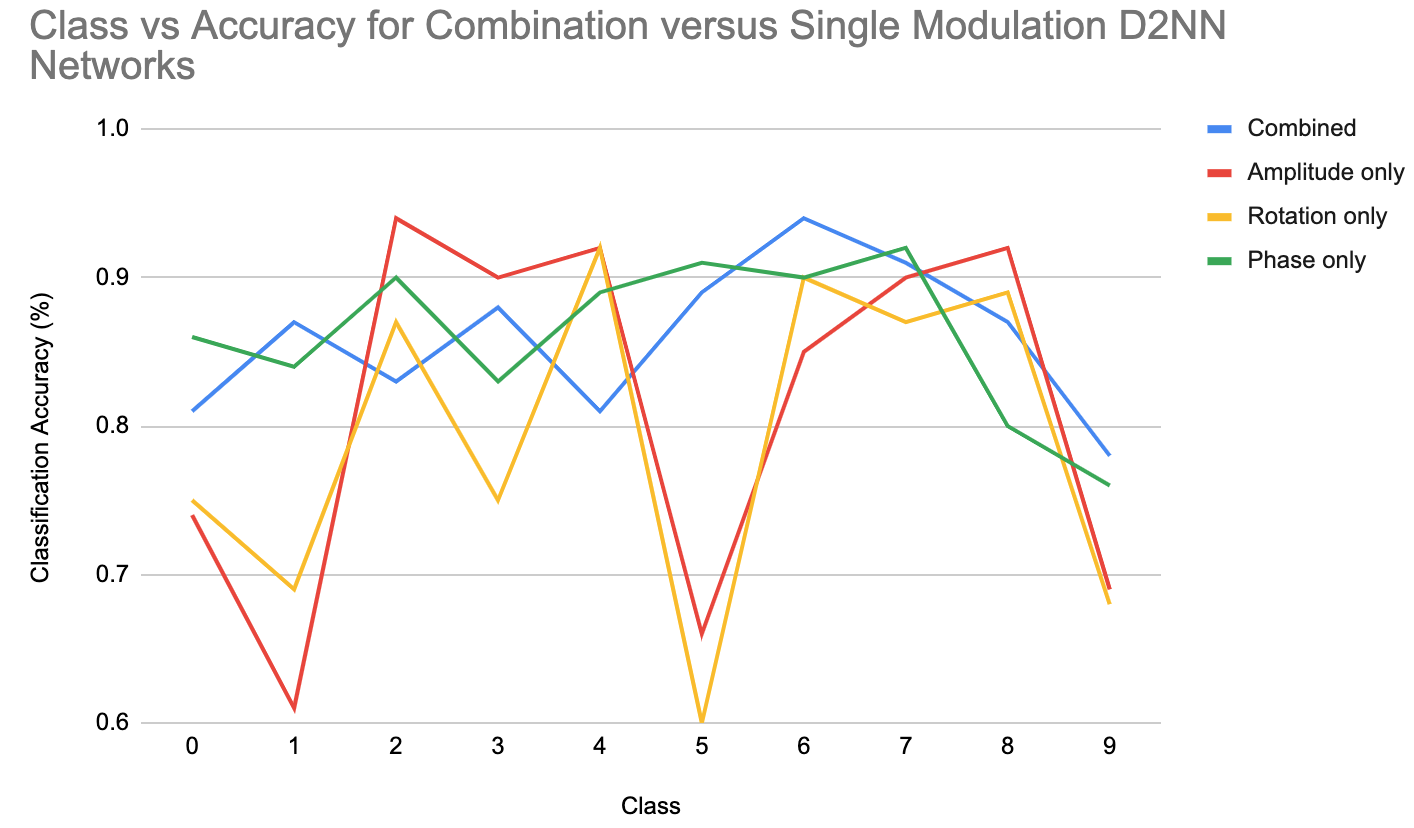
I explored building Deep Diffractive Neural Networks using a combination of phase, amplitude and polarization modulation layers through simulation of coherent visible light. The results for Combination D2NNs for classification and spatial differentiation were preliminary and were not published. I have lots of code and results to show and am open to discussing them. They can be found here
[1] Trabelsi, et al. “Deep Complex Networks.” ArXiv.org, 25 Feb. 2018, arxiv.org/abs/1705.09792.
[2] Lin, et al. “All-Optical Machine Learning Using Diffractive Deep Neural Networks.” ArXiv.org, 26 July 2018, arxiv.org/abs/1804.08711.
